COST
OPTIMISATION
"Cost optimisation is not only fundamental
to the bottom line of the business
but it could be the way you can fund your scale."
Scaling a business requires the
execution of a simple formula:
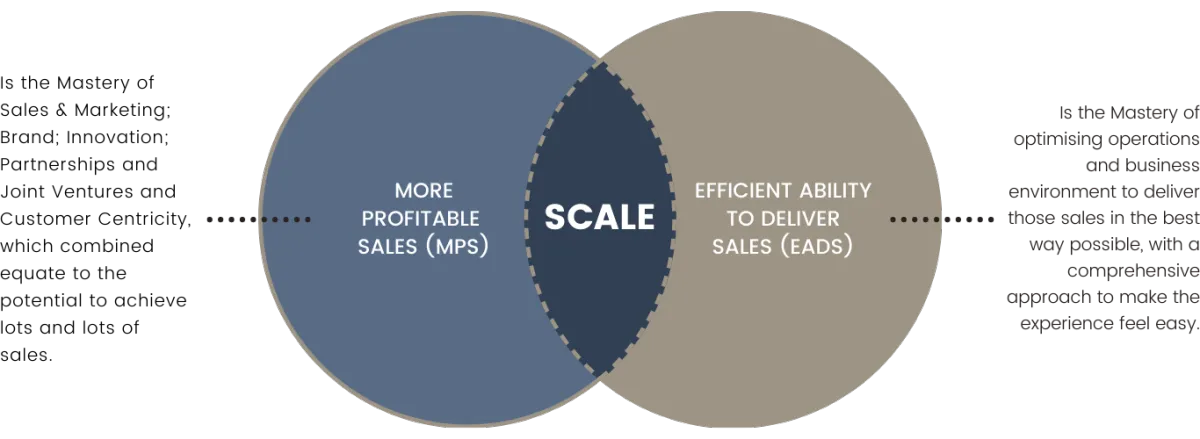
As an organisation trying to scale, you will need to allocate financial resources to both MPS and EADS. To achieve the leanest utilisation of financial resources, you therefore must invest in COST OPTIMISATION.
As much as you need to focus on attaining profitable sales, you must ultimately ensure efficient delivery. Efficiency is not just in form of time efficiency but also cost-efficiency. Too often businesses that generate a lot of cash flow fall victim to cost inefficiencies. They have grown to the scale they are at because they are highly aware that to scale you need to invest in talented resources, assets, tools, marketing etc.
Cost Optimisation is not the same
philosophy as Cost Reduction.
These two concepts are often mistakenly interchanged for each other, however, are somewhat different.

Our philosophy for scaling is that Cost Reduction initiatives are counterintuitive and are dangerous for an organisation if the approach taken is not aligned with strategy. Whereas best practice approaches for Cost Optimisation generate much stronger outcomes and in some regard organically create cost reduction outcomes indirectly.
TO ILLUSTRATE,
SUPPOSE THE COST
STRUCTURE OF AN
ORGANISATION
INVOLVED:

A COST REDUCTION INITIATIVE WOULD LOOK AT THESE COSTS FROM A PERSPECTIVE OF:
a) What can I reduce my headcount to? How many FTEs do we really need right now if we disperse the work?
b) The advertising budget is x, let's liaise with the marketing team to reduce the advertising budget to y.
A COST OPTIMISATION APPROACH WOULD LOOK AT THESE COSTS FROM A PERSPECTIVE OF:
a) For the strategic initiatives we have on at the moment, do we need the activities being conducted by the human capital to take place? How effective is the Talent in performing those activities? Where is there wasted effort and time by the Talent?
b) Looking at the last 20 advertising campaigns run, only 4 of them performed and returned an ROI. What is the root cause of why the others did not perform? Do we have the correct capability to achieve a high ROI when we spend on advertising? What else is preventing the spending from achieving a maximum ROI?
So how should we view costs and cost structures in a business?
1. Necessity
This is the deep identification of why the expenditure is necessary. Most expenditure continues to reoccur because assumptions are made that the expense is needed. A large organisation can easily lose sight of why some of their thousands of transactions are needed.
2. Attribution
This is the ability to attribute the expenditure to the expected benefit, so a return on investment can be calculated (the most common practice to manage this attribution is the use of cost centres). However, attribution is complex and can provide misleading cost analysis if done incorrectly.
3. Opportunity
This is the notion of acknowledging that not all expenditure is necessary; some are voluntary to create opportunity and therefore need to be judged on a different set of criteria than expenditure on necessities.
4. Procurement
Costs may be necessary or voluntary; however, this is the acknowledgement that they may be plenty of suppliers. Procurement practices are in place to prevent purchasing bias and risk, but also to have the support that due diligence was performed to attain the best price for the expenditure. Organisations that have gone down the path of using preferred vendors to minimise purchasing risk now face new problems in purchasing bias leading to overstated prices. Cost optimisation is about attaining the right balance of these things.
5. Budgeting
The practice of setting a budget allows for visibility of expected costs. It reduces surprises and is a required function if controls over expenditure are to work effectively. Contrary to popular belief, being over budgeted on items is not in itself an indication of poor cost optimisation; the budget variance analysis needs to go deeper than this. Overs and under do not provide the full story of expenditure. A business needs to ensure their budget variance analysis can identify decision rationalisation behind the spending to see if cost optimisation has been compromised.
6. Controls
As a scaled organisation there is a need for many employees to have authority to spend on behalf of the business. Centralising expenditure through one department or a few key personnel is inefficient. However with this need for financial empowerment arises a financial risk of employee fraud, unauthorised spending, and accidental cost overruns. Financial controls are an important aspect of cost optimisation as much as it is for cost reduction.
7. Accuracy
Calculating a return on investment (ROI) appears a straightforward calculation however it is not. Therefore the accuracy of the cost analysis needs to be considered. To go deeper with the calculation, to increase accuracy, more focus needs to be made on the benefits side of the equation. Ascertaining the cost component of the ROI calculation is usually more straightforward, as it is the raw expenditure plus perhaps incidental associated costs connected to the item. The benefits however are often miscalculated. Common mistakes are the inclusion of perceived benefits, where the probability of realisation is low; and the omission of hidden cost savings as the extent of the indirect costs of the item is misunderstood.
8. Strategic alignment
Cost reduction usually is performed irrespective of strategy, which is the danger of this approach. Cost optimisation is performed in alignment with strategy. The theory of an expenditure that is "optimised" is because it is spent, with a strategic purpose and is expected to yield the maximum benefit in the context of that purpose.
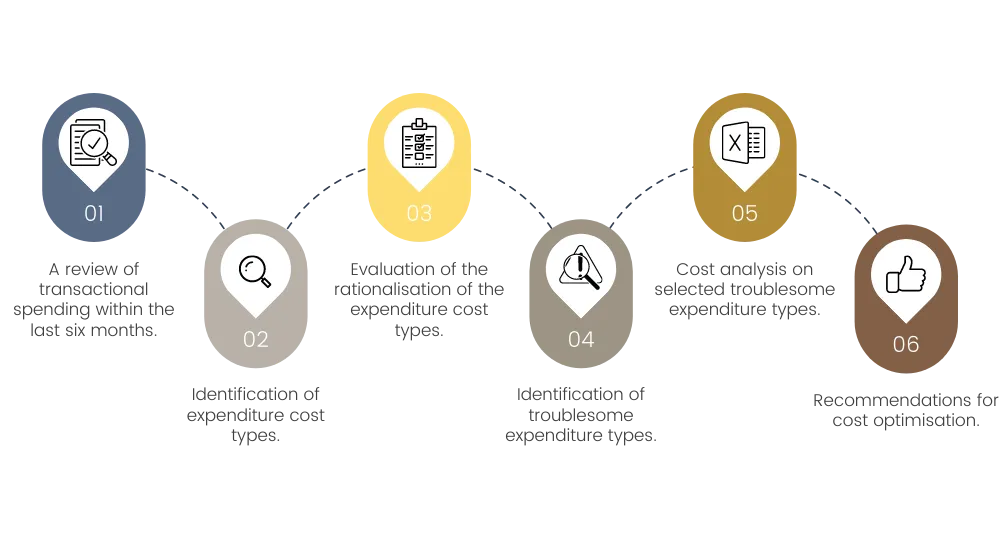
Cost Optimisation Process
A cost optimisation review includes the following steps:
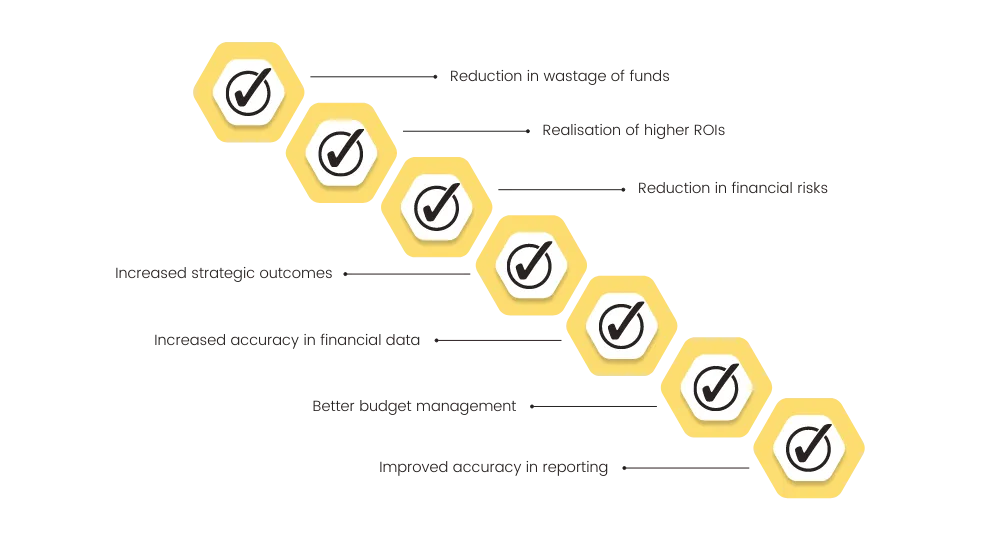
Why undergo a cost optimisation project?
CONTACT US
Have more questions about cost optimisation?
Book in for a 15min chat or send us a message.
FREE MINI SCALING DIAGNOSTIC
Uncover how scaleable your Organisation
is currently with our free diagnostic.
FREE SCALING AMBITION SESSION
Book in a complimentary workshop to define your scaling ambition and decipher a specific scaling challenge with us.
Contact Us
scale@intent.do
(03) 9544 4494 | 0421 089 979
Level 2, 700 Swanston St, Carlton VIC 3053
© Copyright 2025. Intent Scale Pty Ltd. All rights reserved.